TRANSPORT
All grinding discs are relatively delicate. Organically glued discs (resin, shellac, rubber) should not be expected to be resistant to hard holding. The following rules must be followed to prevent crumbs, cracking and breakage.
Discs need to be handled carefully against falling or hitting. It is inconvenient to roll the grinding discs. Where this is not possible due to the size of the stone, a soft, flexible surface must be used.
For discs that cannot be handled, trucks or suitable carriers should be used to ensure smooth transportation. Discs must be carefully placed and supported on trucks to prevent them from tipping over and being damaged. Heavy molds or tools should not be placed on the grinding discs.
STORAGE
Discs that will not be used immediately after the robust packaging are opened carefully, visual control and sound test are taken into the warehouse. The shelves where the discs will be stored should be in dry places, where there is no excessive temperature change, and where it is ensured that they are not exposed to moisture and other liquids. There is a possibility that excessive heat and moisture may damage the structure of the binding agents in the discs. For example, there is condensation in the structure of the disc that is taken from a cold place and operated in a warm environment. Moisture damages the durability of organic binder discs. In inorganic binder discs, the structure of the disc is damaged due to the difference in the expansion number. On the other hand, discs with binders such as resin rubber shellac may oxidize when exposed to moisture.

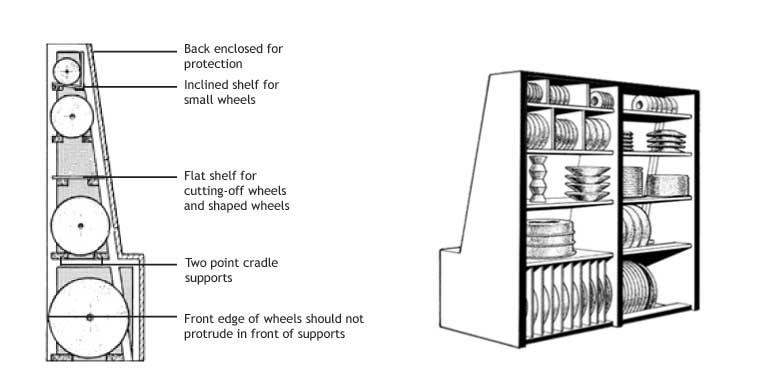
The various types of discs used should be stored in appropriate frames, boxes or partitioned drawers. Discs should be arranged in such a way that they can be placed and taken on the shelves in a way that does not damage other Discs. Preferably, discs should be kept in storages for a minimum of time. It is recommended to write on the discs the date of purchase from the supplier. Old discs should be used before new ones, and if you are unsure, or if discs have been in storage for more than three years, the manufacturer should be consulted about the suitability for use.
Thin, organic binder discs and cuttting discs can be stacked by laying them on a flat and hard slab, a thick steel sheet or a large ceramic structured disc. Abrasive thin discs with a cloth backing should be put on the cloth in the same way. Thus, the corners of these discs are protected. It is also extremely important to place appropriate separators where the tags touch each other in order to eliminate the difference created by the thickness of the disc.
Wedges should be placed on the front and back to prevent the discs placed vertically on the shelves from rolling. The shelves should be separated by vertical partitions in order to facilitate the removal and placing of discs from the shelves. Discs smaller than 100mm should be stored in drawers or boxes.
Paperboard or blotter papers should be placed between thin-sided cylindrical discs and large bowl discs. Cylinder and flat discs with thick edges and hard structures can be placed vertically on their outer diameters such as flat discs. In order to prevent the edges of soft structured flat and conical discs from cracking and breaking, it is suitable to be placed at the bottom or edge.
Very large discs should be taken back to their own boxes after being inspected and stored in warehouses.


 TECHNICAL INFORMATIONS
TECHNICAL INFORMATIONS